Pre-engineered building (PEB) design involves site analysis, load calculations, and selection of appropriate materials and structural elements, followed by detailed engineering using fabrication drawings and bill of materials. The construction phase includes foundation preparation and on-site assembly, while post-construction focuses on inspections, handover, and regular maintenance to ensure structural integrity.
Once the design and engineering are complete, the steel frame of the PEB structure is prefabricated in a factory. This process involves cutting, bending, and welding the steel beams and columns to create the frame. The prefabrication process reduces the amount of time required on site, and it also ensures that the steel frame is of uniform quality.
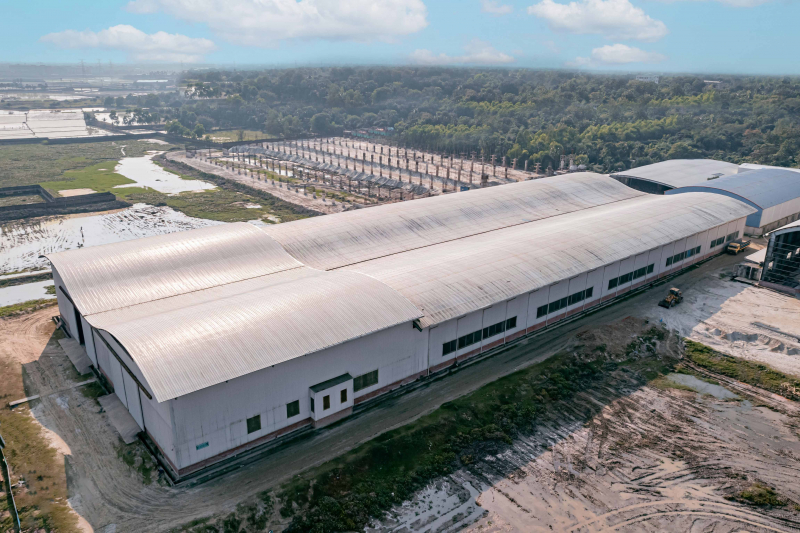
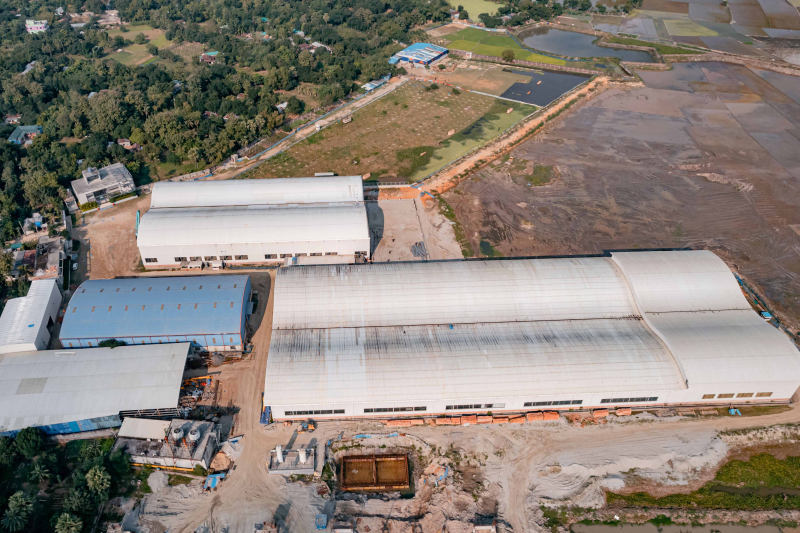
The next step is to erect the steel frame on site. This process is typically done using a crane, and it requires a team of experienced workers. The steel frame is erected one section at a time, and it is important to make sure that it is properly aligned and secured.
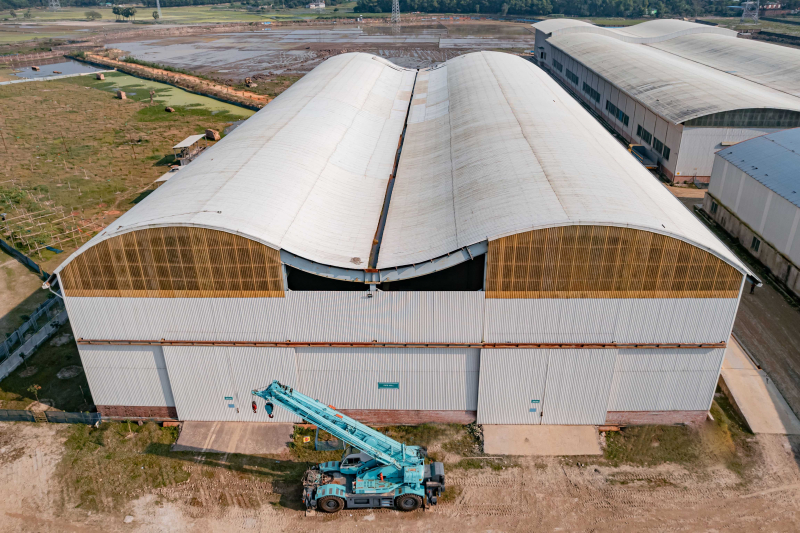
Once the steel frame is in place, the cladding and roofing can be installed. The cladding is the material that covers the exterior of the building, and it can be made from a variety of materials, such as metal, concrete, or glass. The roofing is the material that covers the top of the building, and it can be made from a variety of materials, such as metal, asphalt, or tile.


.webp?token=925a86313ca406231c4da3e8532ed8a9)
.webp?token=fabc3efcb0998e1c588a928fdf2f2bca)


























































.jpg?token=a69777725aa89175b360d4270667bc32)
.jpg?token=6beccffb1198e7b8b29ba7c08bbee06b)
.jpg?token=a9e1f9255c1446ab46979de2929f5064)
.jpg?token=6bdfa2f0139f8fc93fe47e8794d05f97)
.jpg?token=ea98228a38e050a606a60f3cbbf4560f)
.jpg?token=08186f95628227cd372f669ee7fe35b9)



